Understanding Chronic Bilateral Thoracic Back Pain: Causes, Treatment, and Management
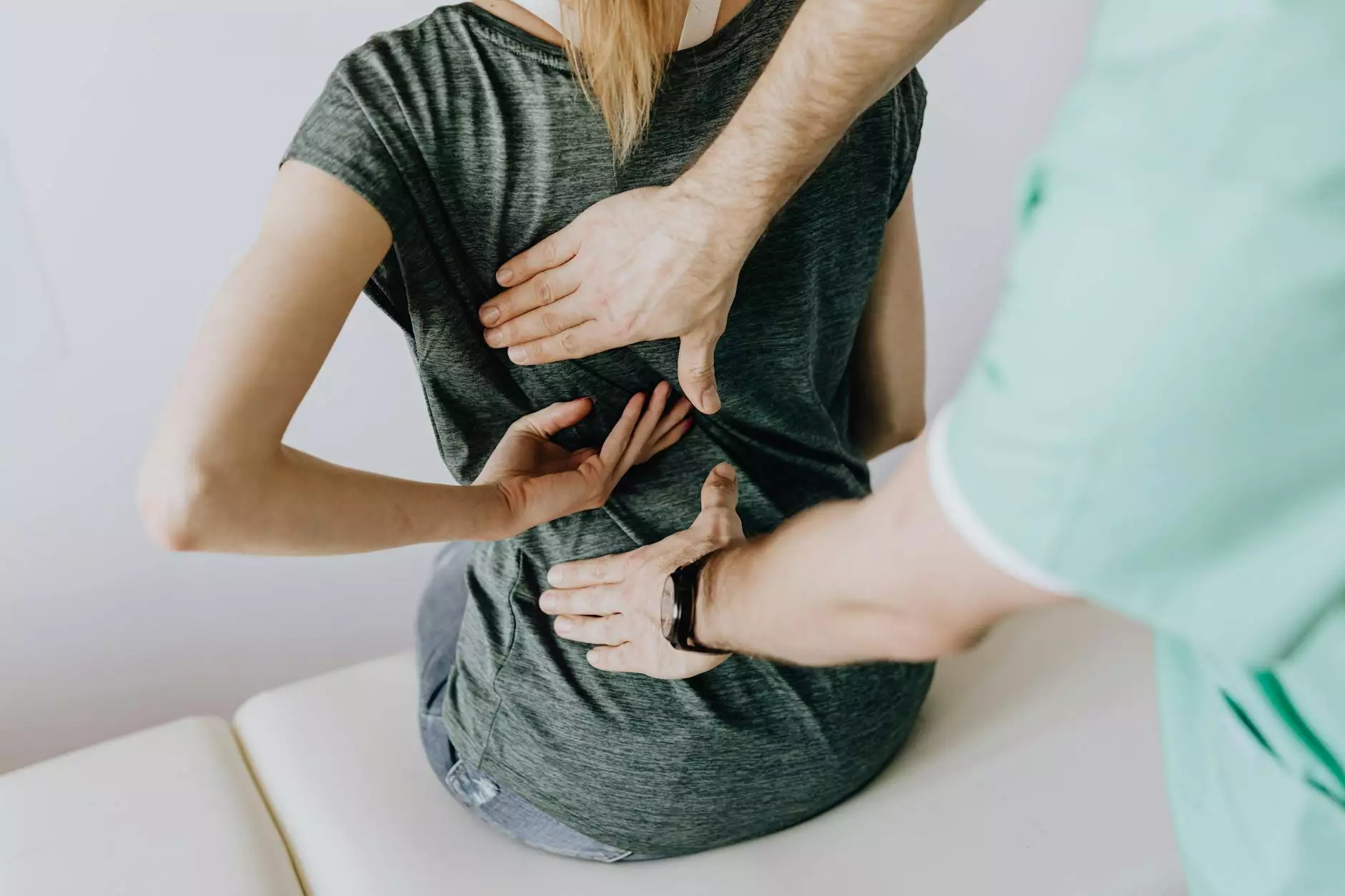

Introduction to Chronic Bilateral Thoracic Back Pain
Chronic bilateral thoracic back pain is a multifaceted condition that affects many individuals, causing discomfort and dysfunction in daily activities. This article serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding this condition, exploring its causes, symptoms, and various treatment options. It aims to equip both patients and healthcare professionals with knowledge that can lead to better management techniques and improved quality of life.
Defining Chronic Bilateral Thoracic Back Pain
Chronic bilateral thoracic back pain refers to persistent discomfort located in the thoracic region of the spine, affecting both sides. Unlike acute pain, which may resolve within a few days, chronic pain lasts for months or even years. This type of pain can significantly hinder mobility and overall well-being.
Identifying the Causes of Chronic Bilateral Thoracic Back Pain
Understanding the underlying causes of chronic bilateral thoracic back pain is essential for effective treatment. Some common causes include:
- Musculoskeletal Disorders: Conditions such as herniated discs, muscle strains, and degenerative disc disease can lead to chronic pain.
- Poor Posture: Extended periods of sitting or standing with improper posture can strain the back muscles and spine.
- Injuries: Previous injuries to the back or spine can cause long-lasting pain if not treated properly.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like arthritis, fibromyalgia, or even infections can contribute to back pain.
- Emotional Stress: Psychological factors, including anxiety and depression, can manifest as physical pain, exacerbating the sensation of discomfort.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The symptoms of chronic bilateral thoracic back pain can vary widely among individuals. Common symptoms include:
- Constant Pain: A steady ache in the mid-back region that does not go away with rest.
- Muscle Stiffness: Feelings of tightness in the thoracic region, especially after periods of inactivity.
- Reduced Mobility: Difficulty in performing daily tasks such as lifting, bending, or twisting.
- Radiating Pain: Discomfort that may spread to the shoulders, neck, or arms.
- Increased Sensitivity: A heightened response to pressure in the affected area.
Diagnosis of Chronic Bilateral Thoracic Back Pain
To effectively diagnose chronic bilateral thoracic back pain, healthcare providers typically perform a detailed assessment that includes:
- Patient History: An in-depth review of the patient's medical history, including any previous injuries or surgeries.
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination to assess posture, range of motion, and areas of tenderness.
- Diagnostic Imaging: X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans determine underlying pathologies within the spine.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests may be ordered to rule out infections or inflammatory conditions.
Treatment Options for Chronic Bilateral Thoracic Back Pain
Effective management of chronic bilateral thoracic back pain often requires a combination of treatments tailored to the individual’s specific needs. Some effective treatment options include:
1. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of treatment for back pain. A licensed physical therapist can develop a personalized exercise program that strengthens the back, improves flexibility, and promotes better posture.
2. Chiropractic Care
Chiropractors specialize in spinal manipulation and may use adjustments to relieve pain and improve spinal alignment. Regular chiropractic adjustments can provide significant relief for many individuals suffering from chronic bilateral thoracic back pain.
3. Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as NSAIDs or acetaminophen, can help manage pain. In some cases, prescription medications may be necessary, including muscle relaxants, nerve pain medications, or anti-inflammatories.
4. Alternative Therapies
Complementary treatments such as acupuncture, massage therapy, and biofeedback have gained popularity for their potential to alleviate pain and promote relaxation. These therapies can be effective adjuncts to traditional treatments.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle changes can have a profound impact on pain levels. Incorporating regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and practicing good ergonomics while at work can all contribute to reducing chronic bilateral thoracic back pain.
The Role of Education in Pain Management
Education about chronic bilateral thoracic back pain is crucial in empowering individuals to take control of their condition. Understanding the anatomy of the back, the impact of posture, and effective pain management techniques can lead to better outcomes. Patient education can involve:
- Workshops on proper lifting techniques.
- Information sessions about the mechanics of back pain.
- Resources on stress reduction and mental health support.
Preventing Chronic Bilateral Thoracic Back Pain
Prevention is always better than cure, especially when it comes to back pain. To minimize the risk of developing chronic bilateral thoracic back pain, consider the following proactive measures:
- Maintain an Active Lifestyle: Engage in regular physical activities, including strength training and flexibility exercises.
- Practice Good Posture: Be mindful of your posture, especially during long periods of sitting or standing.
- Ergonomic Workspaces: Create a workspace that promotes good posture and reduces strain on the back.
- Use Proper Techniques: When lifting heavy objects, use your legs instead of your back to avoid strains.
- Manage Stress: Incorporate stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or meditation to help alleviate tension.
The Impact of Chronic Bilateral Thoracic Back Pain on Quality of Life
The effects of chronic bilateral thoracic back pain extend beyond physical discomfort. Many individuals experience emotional and psychosocial ramifications, including:
- Depression and Anxiety: Persistent pain can lead to feelings of hopelessness and anxiety.
- Social Withdrawal: Individuals may avoid social situations due to discomfort or embarrassment about their condition.
- Impact on Employment: Chronic pain can result in absenteeism, reduced productivity, and ultimately a negative impact on career advancement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, chronic bilateral thoracic back pain is a complex condition that can significantly impact an individual's life. Understanding its causes, seeking appropriate treatment, and employing preventive measures can pave the way for recovery and improved quality of life. It is essential to remember that pain management is a journey that often requires a multifaceted approach involving healthcare providers, education, and personal commitment to self-care and lifestyle changes.
Take Action Today
If you or someone you know is suffering from chronic bilateral thoracic back pain, take the first step toward relief. Consult with a healthcare professional to discuss symptoms, receive a proper diagnosis, and explore treatment options tailored to individual needs.